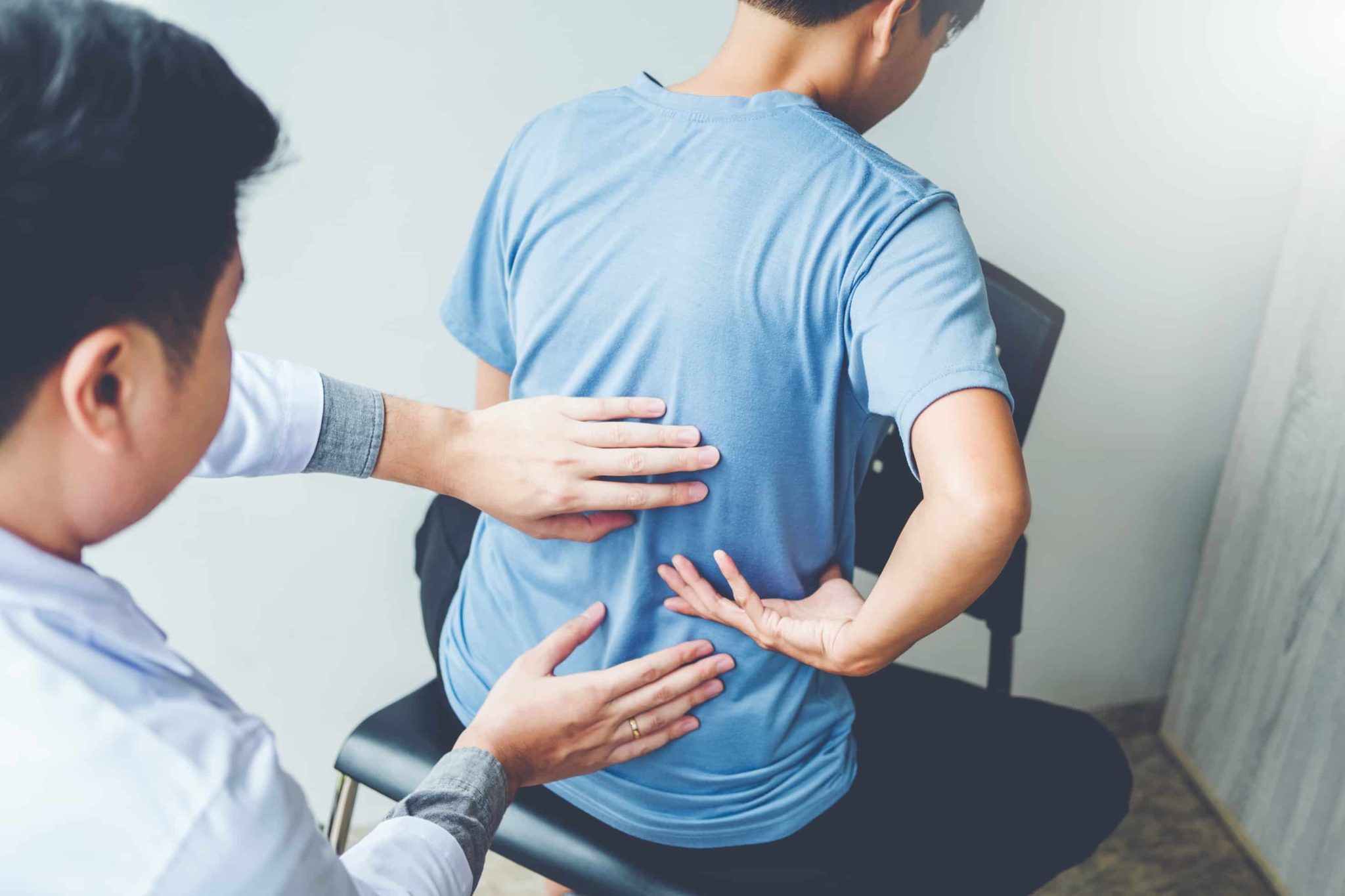
How to Prevent a Workplace Injury
You may believe that working in a comfortable, climate-controlled office is safe and risk-free, but there are hazards to your safety and health all around you. Slips and falls are the most prevalent workplace accident, accounting for most injuries; however, additional office dangers include sprains and strains, poor workstation ergonomics, and mishaps that are beyond your control. This post will look at ways to prevent workplace injuries that you have greater influence over. The first step in avoiding a workplace injury is to be aware of the types of workplace injuries. This article will first go over what physiology is and the overused principle, SAID, musculoskeletal health, types of injuries from having poor musculoskeletal health, and exercises you can do to help your body prevent a workplace injury.
Workplace Injury and Ways to Prevent One
Physiology
The first thing to understand is physiology. Physiology is the study of how the human body operates. It explains the chemistry and physics of basic biological processes, such as how molecules interact in cells and how organ systems work together. It enables us to comprehend what occurs in a healthy body in everyday life and what goes wrong when someone becomes ill. We then have to look at different principles and injuries like the overuse principle and SAID.
What is the Overuse Principal?
Overuse injuries are a regular occurrence in sports and everyday repetitive actions and can be challenging to detect and manage. A variety of circumstances causes these types of injuries. Below are some of the issues physicians face with overuse injuries including diagnosis, therapy, and understanding why the condition happened.
- The body is unable to adapt and repair tissue due to chronic overuse.
- Repetitive movements lead to microtrauma.
- Longstanding microtrauma is the basis for serious injury.
What is Specific Adaptation to Imposed Demands (SAID)?
The SAID principle stands for “specific adaptation to imposed demands,” It basically says that the body will adapt to the sorts of demands placed on it. Individuals who sit for lengthy periods, for example, will begin to transform and structurally adapt to the demands of sitting. This idea, on the other hand, may be applied to exercise. For example, when people undertake resistance training exercises with light weights for an extended period, their bodies adjust by building higher levels of muscular endurance. However, because they have not trained for it, that same individual is unlikely to be successful at lifting maximum weights for more than a few repetitions. Learn more about the principle below.
- The body continually adapts to its environment
- Changes can occur due to prolonged or repetitive postures and movements.
- SAID leads to pathological changes: Arthritis, sprains, strains, joint injuries.
- The body is constantly reacting to its environment, and certain positions and repetitive movements can lead to long term loss and dysfunction.
What is Musculoskeletal Health?
Musculoskeletal health entails more than being free of musculoskeletal conditions. Musculoskeletal health refers to how well the muscles, joints, and bones operate together without causing discomfort. People with strong musculoskeletal health can do the things they desire with ease and without pain. Conversely, poor musculoskeletal health can exist in the absence of a particular musculoskeletal disorder.
Contributing factors to musculoskeletal injuries:
- Poor fitness
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Poor diet
- Stress level
- Metal health
- Dehydration
- Pre-existing injuries
- Pre-Existing diseases
- Visual Fatigue
- Sleep
What Contributes to Musculoskeletal Health?
Musculoskeletal health is the result of several variables. First, the joints and spine must be sturdy and elastic to support the body to perform various actions. Second, muscles must be strong enough to generate the necessary power to move. Third, bones must be strong enough to resist the blows of daily life without shattering. Fourth, a healthy nervous system must monitor all of this activity and provide coordination and balance. And lastly, good mental health is essential to supply energy and enthusiasm to participate in physical activities. Furthermore, this should be without discomfort, stiffness, or weariness.

Types of Workplace Injuries From Poor Musculoskeletal Health
- Low back pain, neck pain
- Sciatica
- Carpal tunnel and other peripheral neuropathies
- Disc herniation/bulge
- Shoulder injuries/dysfunction
- Chronic muscles fatigue
- Posture syndromes – upper cross syndrome, lower cross syndrome
What are the Benefits of Musculoskeletal Health?
When everything is going well, it is easy for people to overlook their musculoskeletal health. But, above all, it is musculoskeletal health that enables people to live freely. Walking needs both strength and coordination. Simple functions such as writing and eating need dexterity of the hands and wrists. Being able to reach up or bend down helps people perform things like gardening, cooking, cleaning, and working.
In addition to allowing individuals to live their lives, excellent musculoskeletal health includes the development of muscles, joints, and bones that will remain healthy for many years to come. People are increasingly hoping that they will be able to enjoy independent, active, and pain-free lives in their later years. This includes staying in the workforce for many individuals. Most people envision an active retirement free of infirmity and falls. In our aging culture, it is more vital than ever to invest in one’s musculoskeletal health today so that one may enjoy their later years.
What is Posture Syndrome?
Postural syndrome is caused by prolonged postures or situations that might harm joint surfaces, muscles, or tendons. For example, pain can be localized and repeatable when end-range postures, such as slouching, are maintained for long periods.
There are four types of postural alignment deviations. These deviations are Kyphosis, Lordosis, Sway Back, and Flat Back. Posture difficulties develop when the muscles that keep the spine in its correct anatomical position become unbalanced. Two particular syndromes that can cause pain are upper crossed syndrome and lower crossed syndrome.
Upper Crossed Syndrome (UCS)
Upper-crossed syndrome (UCS) is also known as proximal or shoulder girdle crossed syndrome. UCS is tightness of the upper trapezius and levator scapula on the dorsal side intersects with tightness of the pec major and minor in UCS. In addition, weakening of the deep cervical flexors overlaps with weakness of the middle and lower trapezius ventrally. This pattern of imbalance affects the atlanto-occipital joint, C4-C5 segment, cervicothoracic joint, glenohumeral joint, and T4-T5 segment.
Lower Crossed Syndrome
Lower crossed syndrome is characterized by weakness of the trunk muscles (rectus abdominis, obliques internus abdominis, obliques externus abdominis, and transversus abdominis), as well as gluteal muscular weakness (gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus). The activation of the superficial muscles inhibits and substitutes for these muscles.
This muscle imbalance causes joint dysfunction, joint pain, and specific postural changes such as anterior pelvic tilt, increased lumbar lordosis, lateral lumbar shift, external rotation of the hip, and knee hyperextension. It can also cause changes in posture in other sections of the body, such as increased thoracic kyphosis and cervical lordosis.
Workplace Ergonomics Can Help Reduce the Chance of a Workplace Injury
Office employees spend several hours a day seated at a desk, working on a computer, which causes ergonomic strains and other problems connected to posture and repetitive movement. Unfortunately, these kinds of dangers might be difficult to see.
To support the largest range of work styles, a choice of adjustable seats, workstations, keyboards, and so on should be available to prevent a workplace injury. Employees should be instructed on how to set up and use adjustable equipment to get the optimal workstation fit.
Proper Ergonomics for Sitting at a Desk
- Shoulders back and relaxed vs. shoulders rolled forward
- Back elongated and supported by proper lumbar support
- Seat back slightly reclined (100 degrees)
- Feet flat on the floor
- Computer monitor(s) straight ahead and at eye level
- Arms at 90 degrees and elbow at sides
- Neck elongated
- Chin tucked vs. chin jutted out
- Diaphragmatic breathing
Micro Breaks Decrease Micro Trauma
Taking micro-breaks is a great way to help your body stay injury-free. Guidelines say that every 30 minutes spent sitting, 2 minutes should be spent moving. By taking breaks, you can decrease pain and injury. Additionally, taking breaks helps increase productivity and well-being, making both employees and employers happier. Micro breaks involve:
- Stretching
- Walking
- Exercise
- Hydrating
If your office or workplace has a private area where you can stretch to ease tension from your body, take advantage of the space to prevent a workplace injury. If you do not have a space to stretch at work, be sure to take time to stretch and ease the day’s tension when you get home from work. Below are some simple upper and lower body stretches that you can do.
Upper Body Stretches to Prevent Workplace Injuries
Cat and Camel Stretch
Step 1: Push yourself up onto all fours and into a tabletop posture. Your hips should be directly over your knees, your shoulders should be directly over your elbows, and your elbows should be directly over your wrists.
Step 2: Lift your head, chest, and sitting bones as you inhale, allowing your tummy to sink and arching your back.
Step 3: Exhale by rounding your spine toward the sky and releasing your head into Cat position.
Step 4: Continue to take deep breaths while shifting your breath, inhaling as you arch your back and exhaling as you round your back.
Brugger’s Stretch to Prevent a Workplace Injury
Step 1: One of the best things about Bruegger’s stretch is that it can be done while sitting. Begin with your arms straight out and your elbows tucked as far into your sides. Then, sit up straight as well.
Step 2: Begin by extending your arms outward, attempting to squeeze your shoulder blades together. To complete Bruegger’s stretch correctly, imagine you have a pencil between your shoulder blades that you don’t want to fall to the ground.
Step 3: Hold this “pinch” for around 5-10 seconds before releasing it. This can be done for around 4-5 sets. Maintaining this pinch may feel a bit unpleasant, but be careful not to overdo it. We’re attempting to open up your shoulders while simultaneously strengthening your upper back muscles. We are assisting you in making healthy posture a normal part of your life by doing so.
Upper Trapezius Stretch
Step 1: Sit up straight in your chair, with your head and neck in a neutral position and your ears aligned with your shoulders. With your right hand, grip the edge of your chair seat. Tuck your chin gently in.
Step 2: Tilt your head to the left while keeping your eyes straight ahead.
Step 3: Place your left hand on your right side of the head. Pull your head to the left gently. Hold the position for 30 to 60 seconds. To enhance the stretch, apply mild pressure.
Step 4: Bring your head and neck back to a neutral posture.
Step 5: Repeat this exercise twice more or as directed.
Step 6: Switch sides and repeat twice more, or as directed.
Lower Body Stretches
Cobra Stretch
Step 1: Lie facedown, legs stretched and toes pointing.
Step 2: Place your hands slightly below your shoulders, palms down.
Step 3: Slowly elevate your head, shoulders, and chest by pressing your palms against the floor. Feel the stretch over your chest and down the front of your torso.
Step 4: Hold the pose for 10 to 15 seconds and repeat 10 times.
Seated Forward Bend (Chair Exercise)
Step 1: Sit at the edge of a chair in an upright position, feet on the floor torso width apart, hands on knees.
Step 2: Take a deep breath in and sit up straight.
Step 2: Exhale, draw your belly button into your spine, keep your abdominal muscles engaged, start to bend forward.
Step 3: As you are bending lead with your chest, keeping your head in line with your shoulders.
Step 4: Try to place your palms flat on the floor and remember to keep your back flat and your abdominal muscles engaged.
Step 5: Hold the position for 10 seconds and raise back up, with your back straight, and abdominal muscles engaged.
Step 6: Repeat the stretch 10 times.
Pretzel Stretch
Step 1: Lie on your left side, with your head on your left arm.
Step 2: Bend your right hip and knee as far as you can toward your chest, then let it fall to the floor.
Step 3: Bend your left knee and grip your left foot with your right hand (use a strap if you can’t reach it).
Step 4: Maintain a straight line with your leg and body as you softly lower your upper shoulder blade to the floor.
Step 5: Turn your head to look over your right shoulder for a deeper spinal twist.
Step 6: Hold for 30 seconds before repeating on the other side. Repeat this stretch 4 times on each side.
Can’t Stretch it Out?
If you are not able to perform the stretches necessary to help alleviate pain you may be feeling its best to seek treatment from a professional.
- Seek a professional team like Evexia Family Chiropractic who can help diagnose the issues and treat the complaint.
- Research indicates that combined therapy has the best outcomes.
- Chiropractic Treatment
- Physical therapy
- Massage
- Medical interventions
Treatment Options for Musculoskeletal Conditions
Speak with a healthcare physician if pain is interfering with your everyday activities or your ability to function. If you are in significant pain as a result of a sudden accident, get medical attention right away. Musculoskeletal pain can be uncomfortable and interfere with your regular activities. A sudden injury, such as a fractured bone, can produce severe pain. Some patients experience pain as a result of underlying diseases such as arthritis or fibromyalgia. Whether you have acute or chronic musculoskeletal pain, the correct treatment can help you feel better.
A few treatments that provide great relief for musculoskeletal conditions include chiropractic adjustments, kinesiology tape, and dry needling.
Lastly On Preventing a Workplace Injury
Your overall health and wellbeing is Evexia Family Chiropractic’s main concern. If you have a job that requires the same motions over and over again or if your job is mostly sitting at a desk, the above article is here to help you prevent a workplace injury. Being aware of your musculoskeletal health and prioritizing stretching is key. Additionally, scheduling an appointment with the experts if you are in any type of pain or discomfort can do wonders. Contact Evexia Family Chiropractic today for Lee’s Summit’s top-rated chiropractic care.